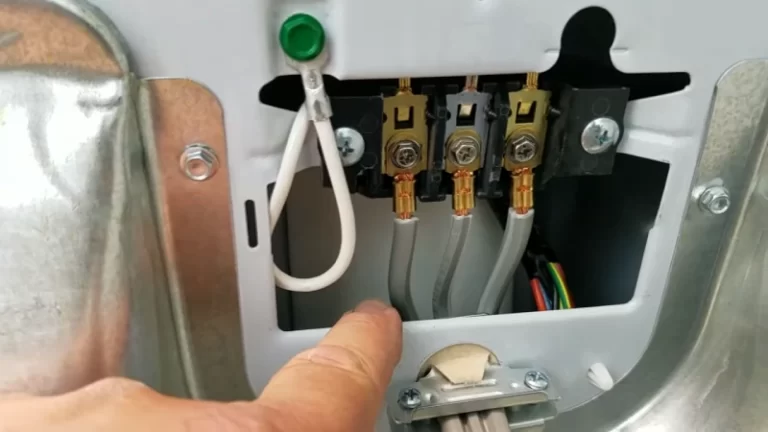
What Size Wire to Run 220V to Garage?
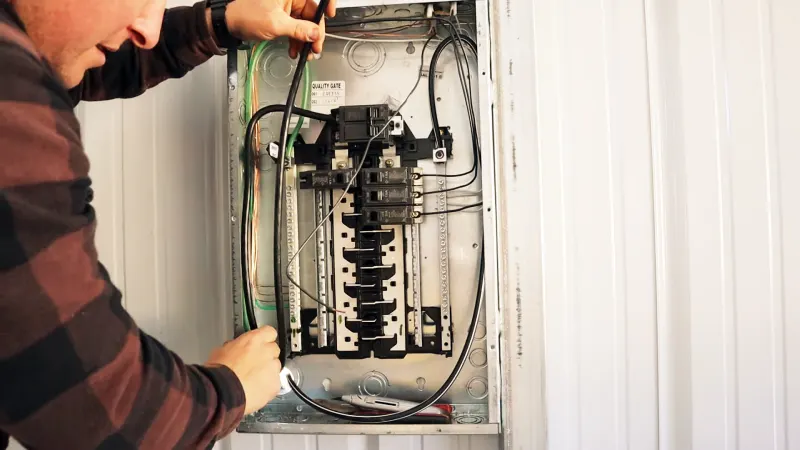
Wiring a garage for 220V is a project that many homeowners can tackle on their own, provided they have the right tools, materials, and knowledge. Running 220V to a garage allows you to use power tools and appliances that require a higher voltage than what is typically available in a residential setting.
This can include heavy-duty tools such as welders, air compressors, and large power saws, as well as appliances such as space heaters and electric water heaters.
In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide for wiring a garage for 220V, as well as some additional tips and information to help you complete the project successfully.
You'll Learn About
Why #6 Cu Size Wire to Run 220 to Garage?
The main reason why #6 Cu wire is used are wire size, grounding, electrical codes, safety, and compatibility.
Wire Gauge
The size or gauge of a wire refers to its width and thickness. In general, the thicker and wider a wire is, the more electrical current it can safely carry. This is because a thicker wire has a larger cross-sectional area, which allows more electrons to flow through it without encountering resistance.
In the case of a welder extension cord, a #6 Cu wire is often used because it is capable of carrying up to 50 amps of electrical current. This is more than enough to power most welding machines, which typically require a minimum of 30 amps of electrical current.
Electrical Code Requirements
Electrical codes are standardized regulations that specify the minimum acceptable standards for the design, installation, and inspection of electrical systems. These codes are designed to ensure the safety of electrical systems and protect people from electrical hazards.
One of the key requirements of electrical codes is the appropriate sizing of wires and circuit breakers. This means that the wire used to run 220V to a garage must be large enough to safely carry the expected electrical load.
The circuit breaker must be sized to protect the wire from overheating and potential fire hazards. In the case of a #6 Cu wire, a 30-amp circuit breaker is typically used.
Grounding
Grounding is a safety feature that is included in all electrical systems. It involves connecting electrical devices and circuits to the earth or to a conductive body that is intended to be an infinite source of zero potential.
This provides a low-resistance path for electric current to follow in the event of a fault or short circuit, which helps to prevent electrical shocks and fires. In the case of running 220V to a garage, a #6 Cu wire is also used for the grounding conductor.
This wire is connected to ground rods, which are long copper or galvanized steel rods that are driven into the ground near the electrical panel. The grounding conductor is then connected to the ground rods and to the electrical panel, providing a low-resistance path for any excess electrical current to flow to the earth.
Safety Features
Welder extension cords are designed to be used in industrial environments, where the risk of electrical hazards is higher than in a residential setting. As a result, they are built with safety features that are not typically found in standard extension cords.
For example, welder extension cords are often rated as SOOW (Service, Oil, and Water Resistant), which means that they are designed to withstand exposure to oil, water, and other contaminants. They are also molded with electroplate copper terminals to prevent surface oxidation, which can cause electrical shorts and other hazards.
Compatibility
Welder extension cords are designed to be compatible with a wide range of welding machines. This means that they have the correct plug and connector types to fit most welding machines on the market, including PrimeWeld, Miller Millermatic, Lincoln Power MIG, Hobart Handler, Ironman, and Betamig welders.
In the case of running 220V to a garage, a #6 Cu wire is also suitable for use as the electrical conductors. This is because it is capable of carrying up to 60 amps of electrical current, which is enough to power most tools and appliances that are commonly used in a garage.
How to Wire Garage Running 220v?
Tools Needed:
- Electrical wire stripper
- Voltage tester
- Wire connectors
- Wire nuts
- Electrical tape
- Conduit and conduit fittings
- Hammer drill
- 1-inch conduit and fittings
- Screwdriver
- Pliers
- Grounding rods and grounding clamp
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Shut off the power to the electrical panel in the house. Use a voltage tester to confirm that there is no electricity flowing to the panel before proceeding.
- Install conduit from the main electrical panel in the house to the location of the garage. This will protect the electrical wire and make it easier to pull through the conduit.
- Use a hammer drill to drill holes for the conduit and install the conduit and fittings.
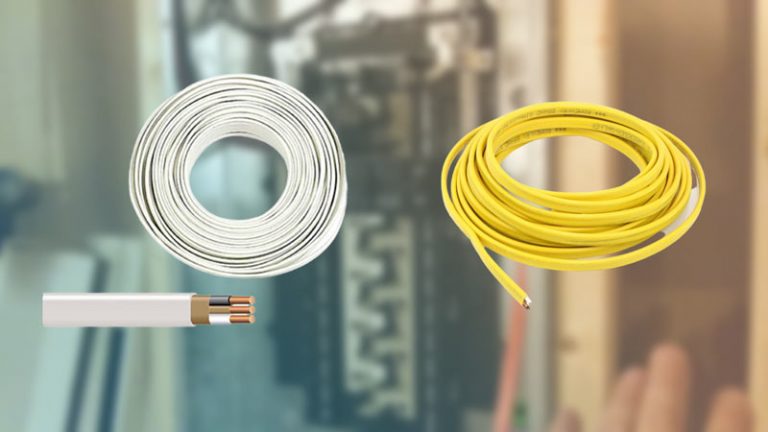
- Pull four electrical wires through the conduit from the main panel to the garage. The wires should be #6 Cu wire, which is capable of carrying up to 60 amps of electrical current.
- At the main panel, connect the two black wires to a 30-amp double-pole circuit breaker. Connect the white wire to the neutral bus bar and the ground wire to the ground bus bar.
- At the garage, install a subpanel to provide both 240V and 120V capabilities.
- In the subpanel, connect the two black wires to the 240V terminal lugs. Connect the white wire to the neutral bus bar and the ground wire to the ground bus bar.
- Install two 8-foot-long grounding rods near the garage and connect them to the subpanel using a #6 Cu grounding conductor.
- Test the electrical system to ensure that it is functioning properly and that all connections are secure.
- Install any desired outlets or appliances in the garage and enjoy your new 220V electrical system.
Additional Tips for Wiring a Garage for 220v
Here are some additional tips for wiring a garage for 220V:
- Always check and follow local electrical codes to ensure that your wiring project is safe and meets all legal requirements.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of the wiring process, it is best to consult with a licensed electrician.
- Before starting the project, make sure you have all the necessary tools and materials, including conduit, wire strippers, wire connectors, and grounding rods.
- When pulling the electrical wires through the conduit, use a fish tape to guide the wires and make the process easier.
- Make sure to properly label all wires and connections, so that you can easily identify them later if needed.
- When installing outlets and appliances, use a voltage tester to confirm that they are wired correctly and that there is no voltage present before touching any wires.
- Use wire connectors and electrical tape to make all connections secure and prevent any exposed wires from causing electrical hazards.
- Regularly test and inspect your electrical system to ensure that it is functioning properly and that all connections are secure. This can help to prevent electrical fires and other hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is it important to run 220V to a garage?
A: Running 220V to a garage allows you to use power tools and appliances that require a higher voltage than what is typically available in a residential setting. This can include heavy-duty tools such as welders, air compressors, and large power saws, as well as appliances such as space heaters and electric water heaters. Some people like to use 8/2 and 8/3 wire for garage heater.
Q: What size wire is used to run 220V to a garage?
A: The size of the wire used to run 220V to a garage depends on the electrical load that is expected to be placed on the circuit. In most cases, a #6 Cu wire is suitable for carrying up to 60 amps of electrical current, which is enough to power most tools and appliances commonly used in a garage.
Correct wire size is very important.
Q: What is the purpose of grounding rods in a 220V electrical system?
A: Grounding rods are used in 220V electrical systems to provide a low-resistance path for excess electrical current to flow to the earth. This helps to prevent electrical shocks and fires by providing a safe outlet for any excess electrical current that may be generated in the event of a fault or short circuit. The wire size for 220V will be different.
Q: Are permits required to run 220V to a garage?
A: In most cases, permits are required to run 220V to a garage. This is because running 220V electrical wiring involves making modifications to the electrical system in a home, which can be a safety hazard if not done properly.
By obtaining a permit, you are ensuring that your wiring project meets all legal requirements and is inspected by a qualified professional to ensure that it is safe. You need to use proper wire too.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wiring a garage for 220V is a project that can provide many benefits, including the ability to use heavy-duty tools and appliances in your workspace.
By following the steps outlined in this article and obtaining the necessary tools, materials, and permits, you can successfully wire your garage for 220V and enjoy the added convenience and functionality that it provides.
It is important to remember to always follow local electrical codes and consult with a licensed electrician if you are unsure about any aspect of the wiring process. With proper planning and execution, you can wire your garage for 220V and enjoy the benefits of having a higher-voltage electrical system in your home.




![Splice 10/3 Wire [is Easy to Do]](/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Splice-10_3-Wire-768x432.webp)
