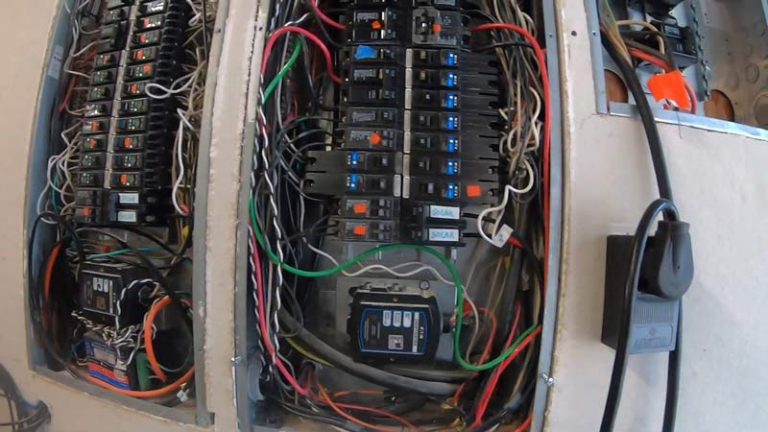
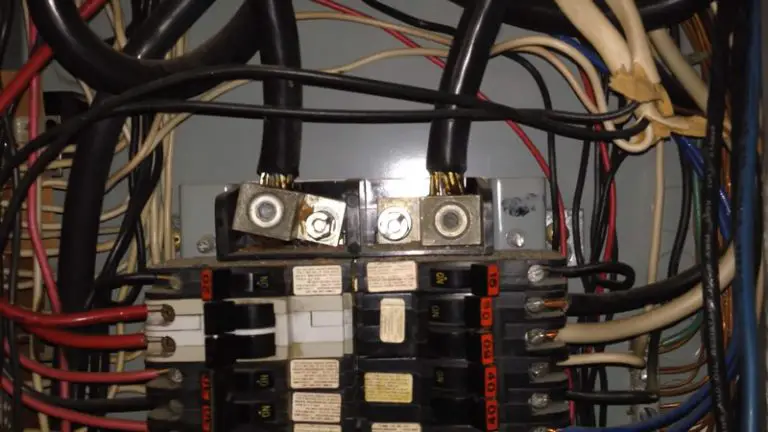
Do Breakers Need to Be Installed for Rough Inspection?
When it comes to electrical installations, understanding the inspection process is crucial for ensuring the safety and compliance of a new system. One common question that arises is: Do breakers need to be installed for rough inspection?
This blog will provide a comprehensive, in-depth look at this topic, explaining the role of breakers during the rough inspection stage, why they matter, and how you can prepare for a successful inspection.
You'll Learn About
Introduction to Rough Inspections
When building a new home, commercial space, or performing significant renovations, the rough inspection is one of the critical stages in the construction process. This inspection ensures that all electrical wiring and systems meet code requirements before the walls and ceilings are closed up with drywall or other finishes.
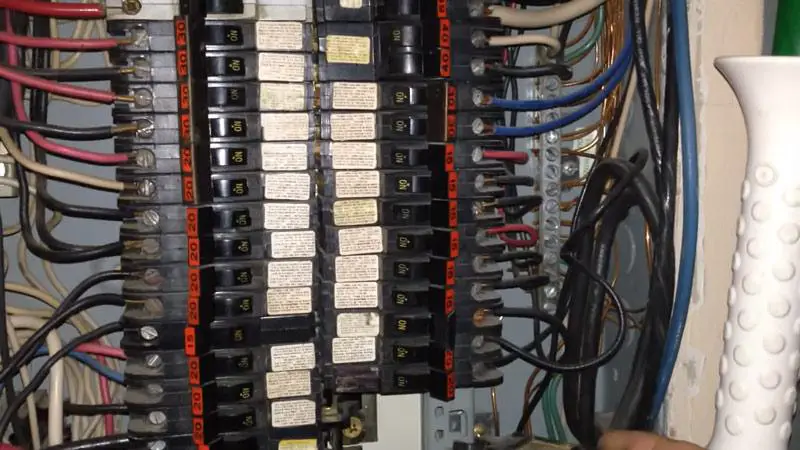

During a rough inspection, electricians and inspectors evaluate the safety, proper installation, and compliance of wiring, conduit, and other critical components. A common question arises: Do you need circuit breakers installed for the rough inspection to pass?
The short answer is: it depends. While breakers may not always be strictly required before a rough inspection, they are often necessary to demonstrate compliance, meet code standards, and show the system’s readiness for final installation.
Let’s break this down further.
Understanding Breakers
To answer whether breakers need to be installed for rough inspections, it’s essential first to understand what breakers are and their role in an electrical system.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device that prevents overcurrent conditions and protects wiring from damage caused by short circuits, overloads, or other electrical faults. Essentially, circuit breakers act as the “off switch” for a circuit, interrupting the flow of electricity when an issue is detected.
They work by automatically detecting unsafe conditions and tripping to stop power flow to the affected circuit.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers come in different types and serve distinct purposes in various electrical systems. Understanding the most common types can clarify their roles during rough inspections:
| Type of Circuit Breaker | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Circuit Breakers | These are the most common types, designed for general-purpose use. | Homes, apartments, and light commercial buildings. |
| Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) | Breakers that protect against electrical shock by monitoring ground faults. | Kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor areas. |
| Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) | Designed to protect against arcing conditions that could lead to fires. | Living rooms, bedrooms, and other areas with wiring. |
| Dual Function Breakers | Combines AFCI and GFCI protection for added safety. | Common in high-risk areas or multi-unit dwellings. |
Each of these breakers offers specific protection mechanisms, and their presence can directly impact a rough inspection’s outcome.
When Are Breakers Required for a Rough Inspection?
To determine whether breakers need to be installed for a rough inspection, it is essential to examine the building codes and electrical system requirements.
Electrical Code Requirements
The National Electrical Code (NEC) outlines standards for safe and compliant electrical installations in the United States. The NEC is updated every three years and governs the rules for wiring, grounding, and circuit protection devices, including the use of circuit breakers.
According to NEC guidelines:
- Breakers should generally be installed when the electrical system is complete enough for a rough inspection.
- Many inspection jurisdictions require the installation of main service panel breakers and individual branch breakers to evaluate wiring safety and adherence to the NEC.
- Some local code requirements may mandate that certain types of breakers (like AFCIs or GFCIs) are installed during rough inspection depending on the intended use or location.
The Role of Breakers in Safety and Compliance
Breakers are more than just safety devices; they demonstrate that:
- The wiring has been installed per code.
- All circuits are properly grounded and protected.
- Electrical circuits are complete enough for the inspector to verify operational safety.
Without the presence of breakers, the inspector has no way to confirm that these systems are functional and in compliance with standards.
Breakers and the Rough Inspection Process
So when should you have breakers installed to ensure the inspection goes smoothly? Let’s explore this.
When You Should Install Breakers Before Inspection
In most cases, installing the main breaker box with branch breakers before a rough inspection is a smart idea. These installations provide the inspector with the tools necessary to evaluate system readiness.
- Main Service Panel Installation: The main service panel, equipped with the main circuit breaker and branch breakers, should be installed and operational for inspection.
- Branch Circuits Wired and Ready: For the rough inspection to verify wiring safety, branch circuit breakers should be in place.
- Code-Specific Requirements: Many jurisdictions require this to ensure proper protection against overcurrent conditions.
Exceptions to the Rule
There are instances where you may not need all breakers installed before inspection:
- When inspection codes explicitly allow wiring inspections before final breaker installation.
- For specific project timelines or construction phases where temporary wiring will suffice until installation is complete.
- If you’re still awaiting specific breaker components or main service panel upgrades.
Preparing for the Rough Inspection: Step-by-Step Guide
Ensuring that you pass a rough inspection requires preparation. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Plan the Electrical Layout
Before any installation, map out the system using the electrical plan and blueprint to ensure that all circuits align with the design.
Step 2: Install Necessary Components
Complete conduit runs, wire installation, and any grounding requirements as indicated by your design.
Step 3: Verify Breakers are Installed (When Applicable)
Install the main service panel with necessary circuit breakers (standard, AFCI, GFCI) per code.
Step 4: Schedule the Inspection
Work with your local inspector or permit office to schedule the rough inspection at the appropriate phase of construction.
Flowchart: Do You Need to Install a Breaker Before the Rough Inspection?
Start
|
v
Is the electrical system ready for rough inspection?
|
Yes --> Is the Main Service Panel and Branch Breakers in place?
|
Yes --> Schedule inspection.
|
No --> Install breakers as per NEC/code.
|
Inspectors approve inspection?
|
Yes --> Pass inspection.
No --> Address findings and reschedule.
When Should Circuit Breakers Be Inspected?
Regular inspections of circuit breakers are essential for safe and efficient operation. Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. Their performance depends on routine maintenance and inspections to ensure reliability and safety.
High-Voltage Circuit Breakers Inspection Schedule
High-voltage circuit breakers require more frequent inspections due to their critical role. These types of circuit breakers should be inspected every six to twelve months. Regular inspections ensure they operate correctly and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
These inspections involve testing the components, connections, and overall system performance. High-voltage circuit breakers are commonly found in industrial or power distribution systems. Inspecting them frequently allows technicians to identify and fix issues early.
Failure to inspect high-voltage circuit breakers regularly can lead to costly downtime. A malfunction in these systems can have severe consequences, including safety risks. Routine maintenance ensures optimal operation and minimizes risks associated with power distribution failures.
Medium-Voltage Circuit Breakers Inspection Schedule
Medium-voltage circuit breakers are slightly less frequent in their maintenance needs. These breakers should be inspected annually or after every 2,000 operations. This schedule provides a balance between regular maintenance and the demands of operation.
Medium-voltage circuit breakers are common in commercial and industrial settings. Their performance is vital for maintaining the safety and stability of the power system. Regular inspection and maintenance can identify wear, corrosion, or component failures in time.
Maintaining these systems annually ensures they function properly and reduces unplanned failures. Performing checks after every 2,000 operations can also catch wear related to frequent usage. Keeping up with these inspections is critical for uninterrupted operations and worker safety.
Why Circuit Breakers Need Routine Inspections
Circuit breakers are vital components in any electrical system, and their failure can lead to costly consequences. They are responsible for protecting wiring and equipment from electrical overloads and faults. Regular maintenance ensures circuit breakers perform their job safely and effectively.
Over time, circuit breakers can wear, lose calibration, or become corroded. Routine inspections identify these issues early and prevent more significant failures. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected downtime and reduces repair costs.
In addition to reducing costs, inspections enhance overall system reliability and safety. Preventative maintenance prevents dangerous failures that can lead to safety hazards or equipment damage. Staying ahead with regular maintenance schedules ensures a safer and more reliable electrical system.
Signs That Circuit Breakers May Need Immediate Inspection
While routine inspections are essential, some signs may indicate immediate problems. For instance, frequent tripping, overheating, or inconsistent operation could mean a malfunction. These signs should prompt an inspection, even if the last routine maintenance was recent.
Corrosion, physical damage, or unusual noises are other warning signs. These issues can compromise the ability of the circuit breaker to function properly. Addressing these warning signs as quickly as possible can prevent catastrophic failures.
Electrical systems should always operate smoothly and without unexpected interruptions. If any of these warning signs are present, schedule a professional inspection immediately. Quick action can prevent further damage and maintain the overall safety of the system.
Circuit Breaker Maintenance Beyond Inspections
Inspections should include more than just visual checks—they should involve comprehensive testing. Technicians often perform diagnostic tests to ensure all components are functioning correctly. This can include thermal imaging, mechanical movement tests, and electrical performance evaluations.
Circuit breaker maintenance includes cleaning connections, replacing worn-out parts, and ensuring proper alignment. Technicians may also recalibrate systems if they have drifted from optimal settings. Preventative maintenance reduces the risk of failures and extends the lifespan of these critical components.
While inspections detect problems, regular maintenance addresses underlying issues directly. Both ensure that circuit breakers will continue to function effectively under changing conditions. Preventative maintenance strategies can save time, money, and unnecessary stress during operation.
The Importance of Professional Inspections and Maintenance
While routine checks can be performed by in-house teams, professional inspections are invaluable. Trained electricians or specialized technicians have the tools and expertise to evaluate circuit breakers thoroughly. They can identify subtle issues that may go unnoticed by less experienced personnel.
Professional inspections use advanced diagnostic tools to assess the performance and condition of the entire system. These tools can detect early warning signs and other irregularities that could lead to failure. Hiring experts ensures that every aspect of maintenance and inspection is accurate and up to industry standards.
Maintaining an electrical system isn’t just about repairs—it’s about proactive management. Investing in professional services provides long-term peace of mind and ensures the safety of equipment and personnel. Circuit breakers perform best when regularly monitored and serviced by qualified professionals.
Conclusion: Preparing for Success
While installing breakers isn’t always strictly required for all inspections, in most cases, having the main service panel with branch breakers installed creates the clearest path to a smooth and successful rough inspection. Breakers are essential safety components that ensure your wiring and circuits are compliant, safe, and operationally ready.
Always follow your local code requirements, collaborate with an experienced electrician, and prepare accordingly to avoid delays or inspection failures.
Breakers are typically required for rough inspections to ensure electrical safety. For more electrical tips, check out our guides on connecting 10-3 to 10-2 wire and pigtail vs daisy chain outlets. If you’re tackling other home improvements, like running wire through a top plate, proper planning ensures compliance.